Enzyme Activity Vs Enzyme Concentration
Enzyme Activity Vs Enzyme Concentration. All proteins are not enzymes and all enzymes are proteins so by quantifying the protein we can know concentration of enzyme in the medium it does not. When cell concentration is around 2.5∼10 × 10 7 cells/ml in inoculation, ethanol production is not affected.
 😎 Reaction rate enzyme concentration. The Effect of the from talisman-intl.com
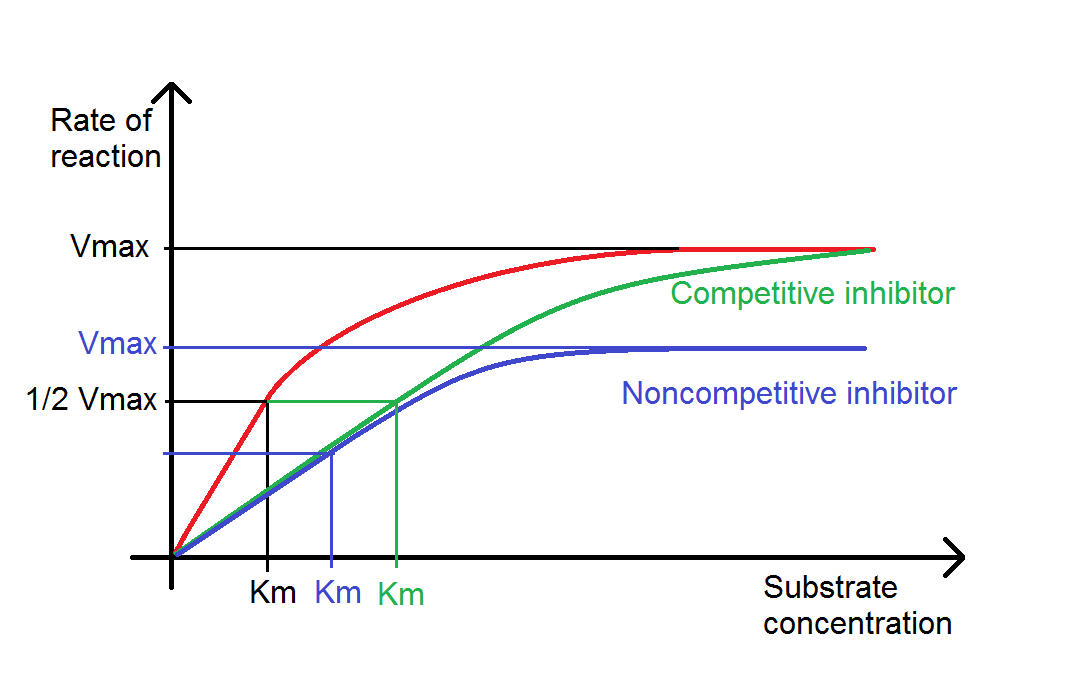
😎 Reaction rate enzyme concentration. The Effect of the from talisman-intl.comSafety ensure eye protection, lab coats and disposable gloves are worn throughout. Significant enzyme activity was seen at 1x enzyme concentration and the ½x enzyme concentration trial showed almost the same activity. Between a and b, the curve represents a zero order reaction;

Significant enzyme activity was seen at 1x enzyme concentration and the ½x enzyme concentration trial showed almost the same activity. Enzyme activity is measured in units which indicate the rate of reaction catalysed by that enzyme expressed as micromoles of substrate transformed (or product formed) per minute.
Enzyme activity= change in od/time taken (min) x 1/extinction coefficient of enzyme x total reaction volume/ volume of enzyme extrct taken x total volume of enzyme extract/ fresh wt of tissue (g. The activity of enzymes is then related to their concentration.

Enzyme activity is generally greatest when substrate concentration is unlimiting. When cell concentration is around 2.5∼10 × 10 7 cells/ml in inoculation, ethanol production is not affected.

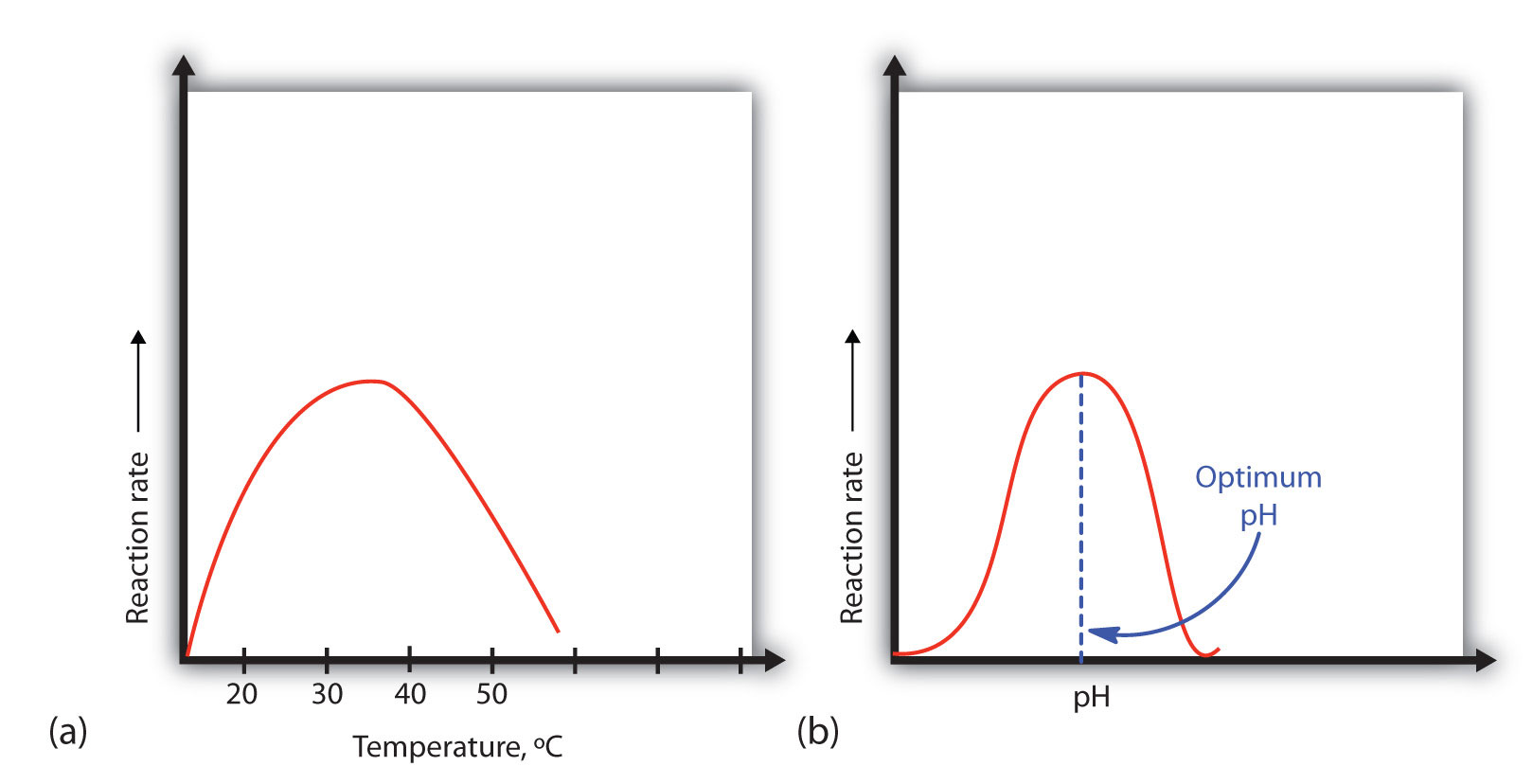
The pancreas releases several enzymes, including proteases, which could be used to investigate the effect of enzyme concentration on initial rate of reaction. The median value of this ph range is called the optimum ph the ph at which a particular enzyme exhibits maximum activity.

Students will perform dilutions to produce the various enzyme concentrations. The activity of enzymes is then related to their concentration.

Rate of reaction of enzyme is directly linked to enzyme concentration, (given that the factors which affects enzyme activity remains constant at a point where trypsin is at active condition) as concentration of enzyme increases, so does the rate of reaction. An enzyme exhibits maximum activity over the narrow ph range in which a molecule exists in its properly charged form.
With the notable exception of gastric juice (the. By using y=mx+c, from your (standard curve) you need to check the concentration of product released in term of micro gram.
What is the relationship between substrate concentration and enzyme activity? The relationship between activity and concentration is affected by many factors such as temperature, ph, etc.

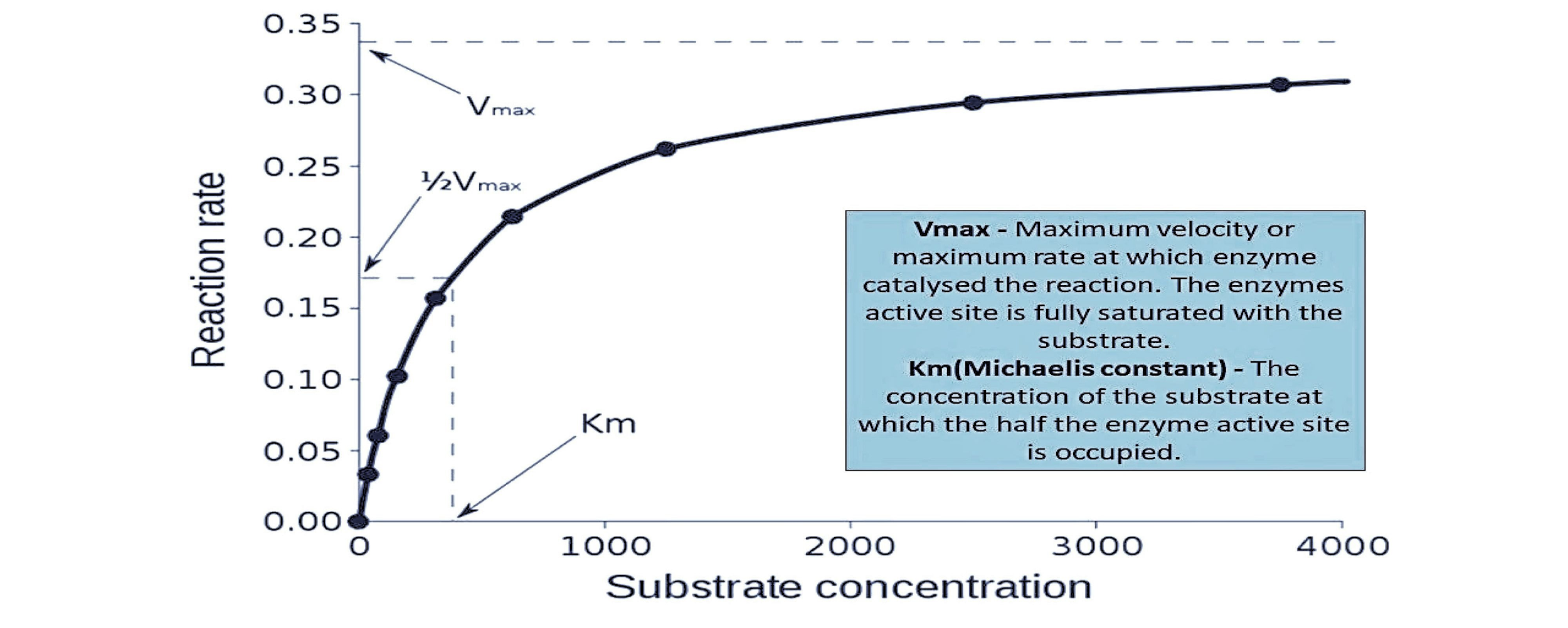
Enzyme activity is measured in units which indicate the rate of reaction catalysed by that enzyme expressed as micromoles of substrate transformed (or product formed) per minute. Increasing substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction.
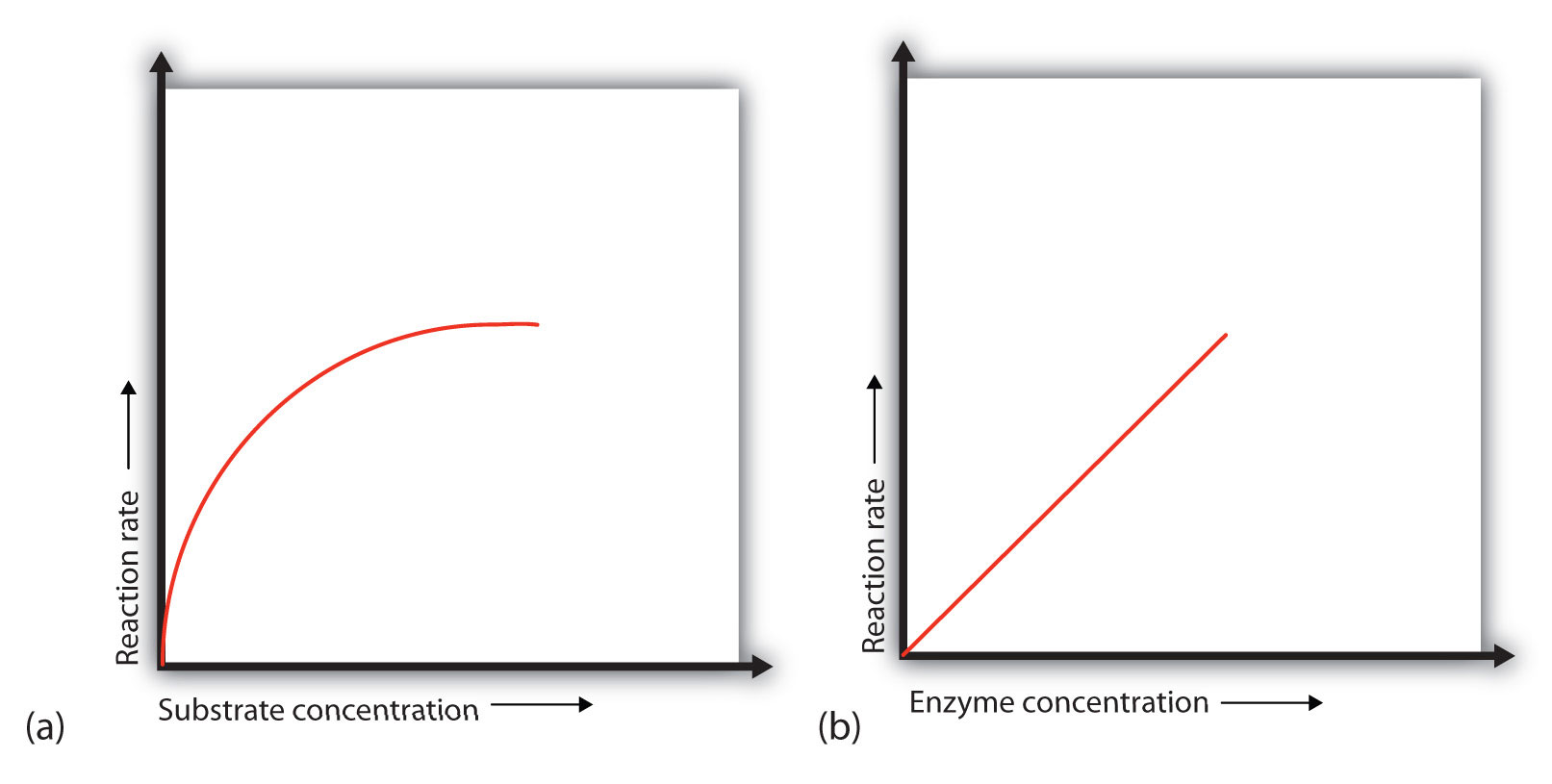
By increasing the enzyme concentration, the maximum reaction rate greatly increases. The relationship between enzyme concentration and enzyme activity is directly proportional.
All enzymes are potential allergens and skin contact should be avoided. An enzyme assay must be designed so that the observed activity is proportional to the amount of enzyme present in order that the enzyme concentration is the only limiting factor.

The relationship between enzyme concentration and enzyme activity is directly proportional. The rate of a chemical reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases.

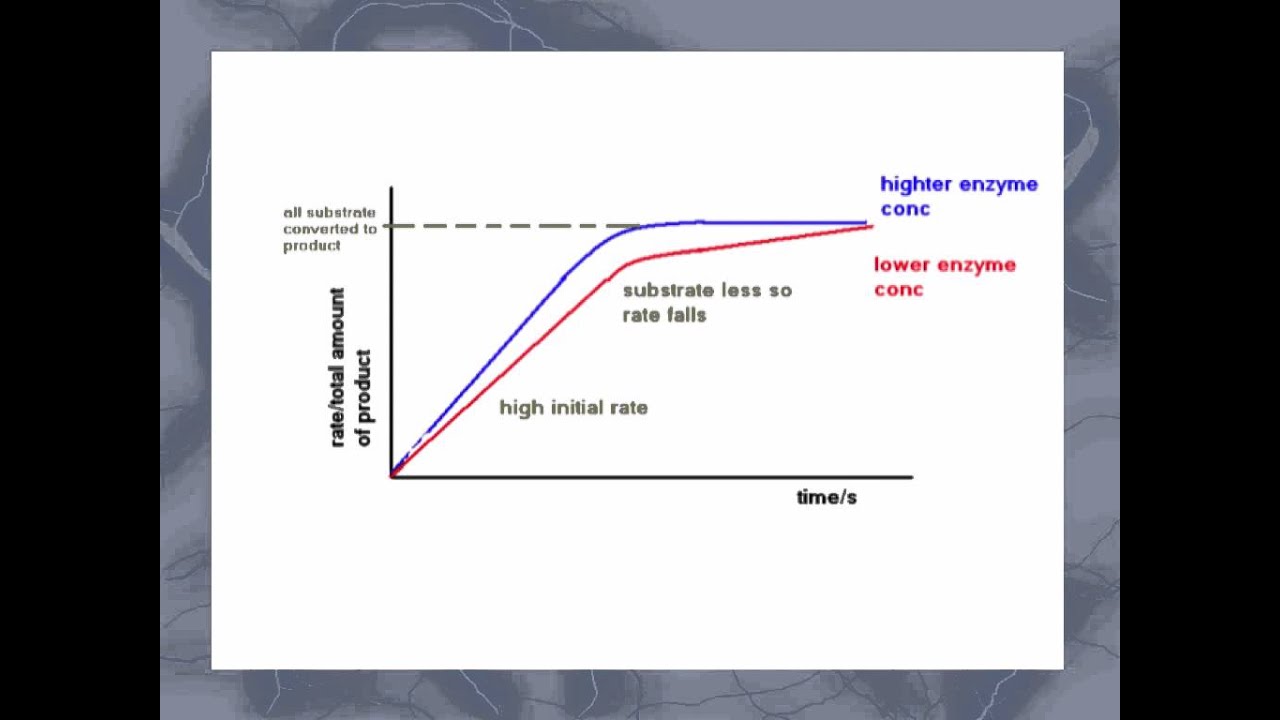
When the concentration of the product of an enzymatic reaction is plotted against time, a similar curve results, figure 6. All enzymes are potential allergens and skin contact should be avoided.
What is the relationship between substrate concentration and enzyme activity? Denaturation, the unraveling or structural changes of an enzyme, may be temporary or permanent depending on the degree of the environmental change.
An enzyme assay must be designed so that the observed activity is proportional to the amount of enzyme present in order that the enzyme concentration is the only limiting factor. Enzyme activity is measured in units which indicate the rate of reaction catalysed by that enzyme expressed as micromoles of substrate transformed (or product formed) per minute.

The relationship between activity and concentration is affected by many factors such as temperature, ph, etc. After identifying the amount of product release, then you can calculate enzyme activity.

Enzymes can greatly speed up the rate of a reaction. With the notable exception of gastric juice (the.
The relationship between activity and concentration is affected by many factors such as temperature, ph, etc. The aim of this activity is to investigate the effect of a reduction in enzyme concentration on the initial rate of reaction.

Rate of reaction of enzyme is directly linked to enzyme concentration, (given that the factors which affects enzyme activity remains constant at a point where trypsin is at active condition) as concentration of enzyme increases, so does the rate of reaction. Finally, we tested the effect of ph on the enzyme with ph 7, ph 1 and ph 11.

All enzymes are potential allergens and skin contact should be avoided. The aim of this activity is to investigate the effect of a reduction in enzyme concentration on the initial rate of reaction.
By Using Y=Mx+C, From Your (Standard Curve) You Need To Check The Concentration Of Product Released In Term Of Micro Gram.Finally, we tested the effect of ph on the enzyme with ph 7, ph 1 and ph 11. The relationship between enzyme concentration and enzyme activity is directly proportional. Rate of reaction of enzyme is directly linked to enzyme concentration, (given that the factors which affects enzyme activity remains constant at a point where trypsin is at active condition) as concentration of enzyme increases, so does the rate of reaction.
How Does Concentration Of Enzyme Affect Enzyme Activity?An enzyme assay must be designed so that the observed activity is proportional to the amount of enzyme present in order that the enzyme concentration is the only limiting factor. The rate of a chemical reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases. If there is higher enzyme concentration with a constant level of substrate (1% h2o2), then enzyme activity/rate will be.
Between A And B, The Curve Represents A Zero Order Reaction;All enzymes are potential allergens and skin contact should be avoided. Significant enzyme activity was seen at 1x enzyme concentration and the ½x enzyme concentration trial showed almost the same activity. The initial concentration of yeast cells.
Students Will Perform Dilutions To Produce The Various Enzyme Concentrations.• a and b changes are negative because the substrates are disappearing • p change is positive because product is being formed. Enzymes are usually present in very small quantities. Enzyme activity is measured in units which indicate the rate of reaction catalysed by that enzyme expressed as micromoles of substrate transformed (or product formed) per minute.
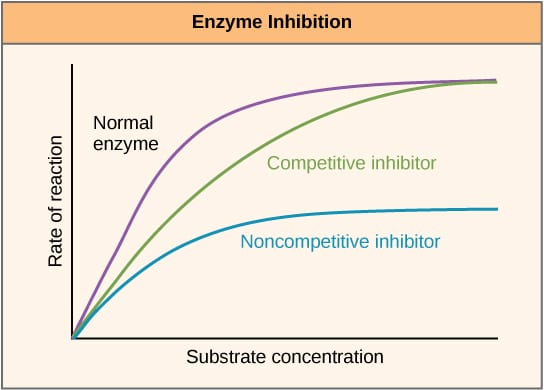
An Enzyme With A High Km Relative To The Physiological Concentration Of Substrate, As Shown Above, Is Not Normally Saturated With Substrate, And Its Activity Will Vary As The Concentration Of Substrate Varies, So That The Rate Of Formation Of Product Will Depend On The Availability Of.• the rateof the reaction catalyzed by enzyme e a + b ↔ p. Enzyme concentration enzyme concentration as enzyme = reaction rate more enzymes = more frequently collide with substrate reaction rate levels off substrate becomes limiting factor not all enzyme molecules can find substrate enzyme concentration rate Denaturation, the unraveling or structural changes of an enzyme, may be temporary or permanent depending on the degree of the environmental change.
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Enzyme Activity Vs Enzyme Concentration"
Posting Komentar